What is abnormal uterine bleeding?
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) refers to irregularities in the menstrual cycle involving disturbances in frequency, regularity, duration, and volume of flow. This causes heavy and irregular bleeding, which does not align with the regular monthly cycle.
For a healthy woman, a normal period typically lasts about five days after every 21 to 35 days with a total blood loss of about 30 to 80 mL (roughly 2 to 5 tablespoons). Bleeding that is excessive, prolonged, or occurs outside of these days is considered abnormal uterine bleeding.
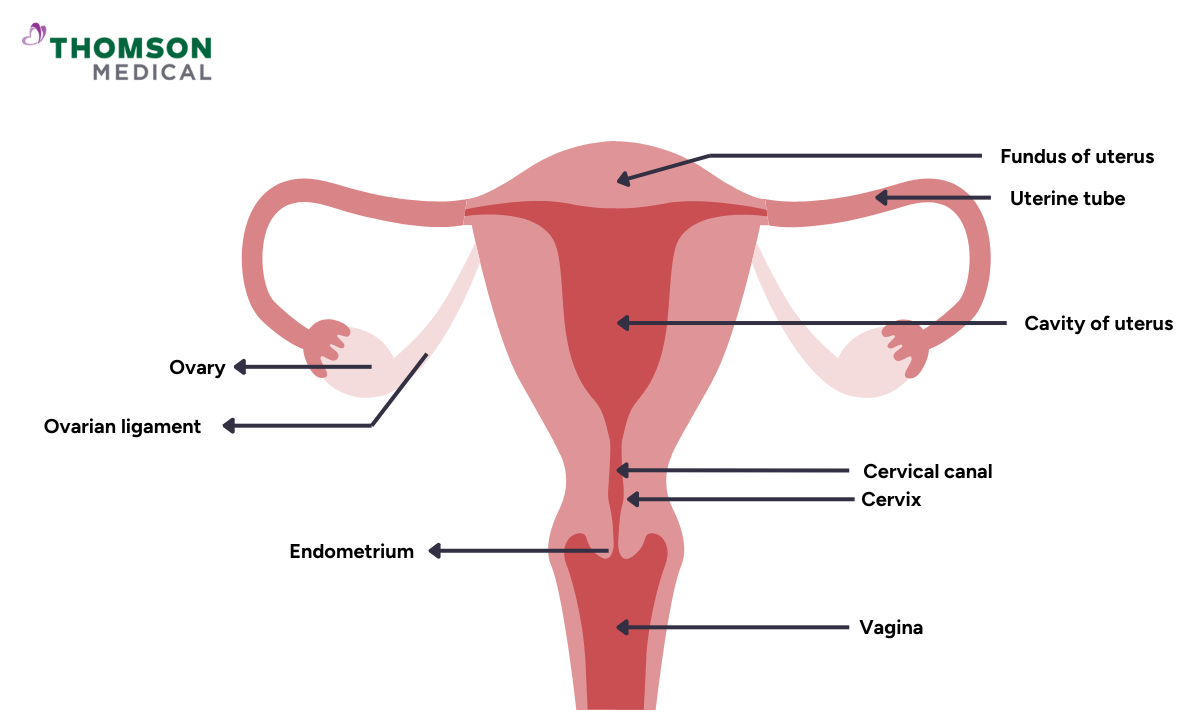
What causes abnormal uterine bleeding?
Common causes of abnormal uterine bleeding can be classified using the PALM-COEIN classification below.
Structural causes (PALM)
P – Polyp
These are small, non-cancerous growths inside the uterus or cervix. Uterine and cervical polyps can cause irregular or heavy bleeding, especially between menstrual periods or after intercourse.
A – Adenomyosis
A condition where the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows into the muscle wall, making periods heavier, longer, and more painful.
L – Leiomyoma (Uterine fibroids)
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous lumps in the uterus, which can cause heavy menstrual bleeding or prolonged periods, pelvic pain, or pressure on nearby organs.
M – Malignancy
Abnormal or cancerous changes in the uterine lining that can cause unusual menstrual bleeding, especially after menopause.
Non-structural causes (COEIN)
C – Coagulopathy
Blood disorders, like clotting problems or conditions such as von Willebrand disease, that lead to heavy and abnormal bleeding during periods.
O – Ovulatory dysfunction
Irregular or skipped ovulation due to hormone imbalances, which can result in unpredictable or prolonged vaginal bleeding.
E – Endometrial
Issues with the uterine lining’s ability to shed properly, causing abnormal bleeding even when there’s no structural problem.
I – Iatrogenic
Menstrual bleeding that is caused by medications (like blood thinners or hormonal treatments) or medical devices.
N – Not Yet Classified
Unusual or rare causes of menstrual bleeding that don’t fit into the other categories and may require more investigation.
If you are experiencing abnormal bleeding, it's normal to feel concerned. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical; our specialists can help to diagnose and find the underlying cause of your health conditions.
What are the symptoms of abnormal uterine bleeding?
Below are the signs that commonly indicate abnormal uterine bleeding in women:
Heavy bleeding (menorrhagia)
Soaking through a pad or tampon every 1-2 hours due to menorrhagia.
Passing large blood clots (larger than a quarter).
Prolonged bleeding
Monthly periods lasting longer than 7 days.
Frequent bleeding
Cycles shorter than 21 days (frequent periods).
Infrequent or irregular periods
Irregular bleeding longer than 35 days (infrequent periods) with unpredictable bleeding patterns.
Bleeding between periods (metrorrhagia)
Spotting or bleeding outside of a typical period.
Postmenopausal bleeding
Any bleeding that occurs after menopause.
Other symptoms
Fatigue or dizziness due to blood loss.
Symptoms of anaemia, such as pale skin or shortness of breath.
If you have menstrual abnormalities such as prolonged menses, heavy bleeding, or bleeding between periods, it is recommended that you see a gynaecologist right away.
How is abnormal uterine bleeding diagnosed?
Abnormal bleeding can be worrisome, but the first step is understanding what’s causing it. A thorough evaluation will help your doctor find the right approach to address your concerns.
Detailed medical history
Menstrual cycle details
Your doctor will ask about the length, duration, severity of menstrual bleeding, and cycle frequency.
Bleeding patterns
You will be assessed by your menstrual bleeding pattern. This section includes questions regarding bleeding between periods and postmenopausal bleeding.
Associated factors
Your doctor will ask if you are taking any blood thinners, hormonal therapy, or contraceptives. Additionally, you will also be asked if you have any prior history of clotting disorders, thyroid issues, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Laboratory tests & screening
Routine blood tests
If you're experiencing abnormal vaginal bleeding, your doctor may order a blood test to exclude iron deficiency, anaemia and thyroid disease as possible causes.
Pelvic ultrasound
To exclude uterine abnormalities such as polyps, fibroids, adenomyosis, precancer (hyperplasia), and cancer as causes of abnormal menstrual bleeding, a pelvic ultrasound is needed.
Cervical cancer screening by PAP or HPV test
A Pap smear test or HPV test helps in precancerous changes or early cervical cancer.

Invasive diagnostic procedures
Dilation and curettage
Dilation and curettage is a procedure that first uses instruments to dilate the cervix, followed by a curette to obtain endometrium to be sent for biopsy. Dilation and curettage hysteroscopy is performed to exclude malignancy and treat abnormalities in menstrual bleeding.
Complications of this procedure include bleeding, infection, abandoned procedure with inability to gain entry into the uterine cavity, damage to the cervix, and scarring of the uterine cavity (Asherman's syndrome)
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a minor surgical procedure that involves looking inside the womb using a hysteroscope, an instrument with a small video camera attached. It can be both diagnostic, for checking uterine abnormalities or confirming malignancy, and therapeutic, for treatment.
Complications can include bleeding, infection, excess fluid in the uterus (fluid overload), or injury to the cervix during insertion.
In rare cases, the uterus may be accidentally pierced (uterine perforation) during the procedure, affecting about 5 in 1,000 women. Most heal on their own, but if needed, a diagnostic laparoscopy can be done. On rare occasions, nearby organs may be injured and require further surgery.
It's essential for patients to inform their gynaecologist about any new or worsening symptoms for accurate treatment. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical to receive personalised care and timely support tailored to your health needs.
Treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding
Irregular bleeding can be treated through various medical treatments, depending on the cause. Here are the common treatments that your healthcare provider can perform, such as:
Medications
Hormonal treatments
Birth control pills and GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) injections regulate periods and help reduce heavy blood flow.
Non-hormonal treatments
Tranexamic acid, which can reduce excessive bleeding.
NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), pain relievers like ibuprofen can help reduce both pain and bleeding.
Iron supplements
For patients with iron deficiency anaemia caused by heavy periods.
Intrauterine device (IUD)
Hormonal IUD
This form of birth control can be used to manage heavy and painful periods. An IUD releases progestin, which is a hormone that helps reduce irregular bleeding and can be effective for up to 5 years.
Minimally invasive surgical procedures
Hysteroscopic surgery
In addition to being used for diagnostic purposes, hysteroscopy is also used as a therapeutic procedure to remove endometrial polyps or submucosal fibroids.
During the procedure, a thin, lighted camera is inserted through the cervix into the uterus, allowing the surgeon to precisely remove abnormal tissue with minimal invasiveness.
Transcervical resection of the endometrium
This procedure involves using a thin instrument inserted through the cervix to remove the endometrial tissue (the lining of the uterus).
By removing the uterine lining, the procedure helps reduce or stop bleeding, and it can be a suitable option for women who do not want to undergo a hysterectomy.
Surgical procedures
Myomectomy
Myomectomy surgery removes fibroids (non-cancerous growths) from the uterus while leaving the uterus intact. This is a good option for women who want to preserve their ability to have children in the future.
Hysterectomy
This procedure involves the complete removal of the uterus, typically used when other treatments have failed or in severe cases of abnormal uterine bleeding.
It is often recommended for women who no longer wish to have children or when the bleeding is affecting quality of life.
Lifestyle changes
Managing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular exercise can help regulate normal periods and improve hormonal balance.
Abnormal uterine bleeding can be associated with various gynaecological conditions. Read more about it here.
FAQs
What does hormonal imbalance bleeding look like?
Hormonal imbalance bleeding can lead to irregular periods, either heavier or lighter than usual, and spotting between cycles. It often occurs due to changes in oestrogen and progesterone levels.
When is period bleeding an emergency?
Period bleeding becomes an emergency if the menstrual flow soaks through a pad or tampon every hour for several hours, large clots are passed, or severe pain and dizziness are experienced. This can indicate a serious underlying issue that needs immediate medical attention.
At what ages is abnormal bleeding more common?
Abnormal bleeding is more common in teenage girls and women approaching menopause, typically in their late 40s or early 50s. Hormonal changes during these stages can disrupt the menstrual cycle.
What are the red flags for abnormal uterine bleeding?
Red flags for abnormal uterine bleeding include excessive bleeding, prolonged periods, irregular uterine bleeding, or bleeding after menopause. Other signs like severe pelvic pain, dizziness, or symptoms of anaemia also require prompt attention.
Is it normal to have blood in your uterus?
It's normal for women to experience uterine bleeding during their menstrual periods. For a healthy woman, a normal period typically lasts about five days, occurring every 21 to 35 days, with a total blood loss of about 30 to 80 mL (roughly 2 to 5 tablespoons). What's not considered as normal bleeding is:
Excessively heavy menstrual flow (soaking through a pad or tampon every 1-2 hours).
Prolonged bleeding (lasting longer than 7 days).
Occurring too frequently (cycles shorter than 21 days).
Irregular uterine bleeding (cycles longer than 35 days).
Happening between periods
Present after menopause
These patterns would be considered unusual bleeding and could indicate underlying conditions such as polyps, adenomyosis, fibroids, hormonal imbalances, or other health issues.
Can stress cause abnormal uterine bleeding?
Yes, stress can affect the hormonal balance, leading to unpredictable bleeding or missed periods. High stress levels can interfere with the menstrual cycle by affecting the pituitary gland's function.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
- Paragon (female doctor): +65 6735 0300
- Woodleigh: +65 8684 0153
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Bukit Batok: +65 6569 0668
- Choa Chu Kang: +65 6893 1227
- Jurong: +65 6262 8588
- Punggol: +65 6243 6843
- Sembawang: +65 6753 5228
- Sengkang: +65 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): +65 6382 3313
- Tampines: +65 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: +65 6276 1525
Dr Ryan Lee Wai Kheong
Obstetrics & Gynaecology (O&G)
Thomson Specialists Woodleigh (Women's Health)
English, Mandarin
Adept, MHC, HSBC, Alliance MediNet and 1 other

.png%3Fbranch%3Dprod&w=3840&q=75)