Gum recession can expose the tooth roots, leading to increased sensitivity, a higher risk of decay, and aesthetic concerns. What’s important is getting the right treatment of gum grafts to maintain and restore your gums to halt the progression of gum recession.
What is receding gum?
Receding gum, also known as gum recession, is a condition where the gum tissue gradually pulls away from the tooth, exposing more of the tooth surface or even the root beneath.
This process often happens slowly and may go unnoticed at first. While it is a common condition, it should not be ignored, as untreated gum recession can progress over time and affect the long-term stability of your teeth.
Why do gums recede?
Gum recession usually develops over time and is often the result of one or more contributing factors rather than a single cause.
Gum disease (periodontal disease)
Ongoing inflammation caused by plaque and bacteria can damage the gum tissue and the bone supporting the teeth, leading to gradual recession.
Aggressive or improper brushing
Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear away gum tissue over time, especially along the gumline.
Smoking and vaping
Tobacco and nicotine reduce blood flow to the gums and weaken the body’s ability to maintain healthy gum tissue, increasing the risk of recession.
Naturally thin gums (genetic factors)
Some people are born with thinner or more delicate gum tissue, making them more susceptible to recession even with good oral hygiene.
Teeth grinding or clenching (bruxism)
Excessive forces on the teeth can place strain on the gums and supporting bone, contributing to tissue loss.
Misaligned teeth or dental restorations
Teeth that are out of alignment or poorly fitting crowns and fillings can create uneven pressure and make certain areas more prone to gum recession.
How to treat receding gums
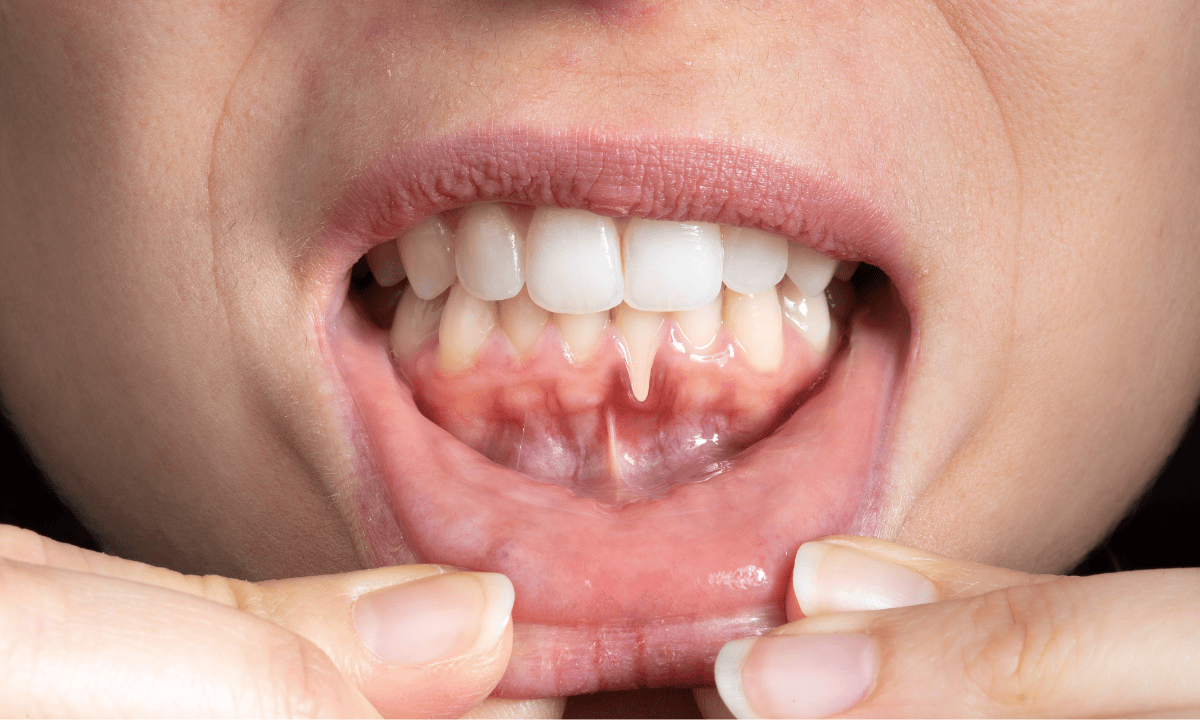
The treatment for gum recession depends on its severity and the extent of tissue and bone loss.
In mild cases, your dentist may recommend deep cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing. This procedure involves carefully removing plaque and tartar buildup from the tooth surfaces and exposed roots below the gum line. The root surfaces are then smoothed to make it harder for bacteria to reattach.
When your dental condition is more advanced and cannot be adequately managed with deep cleaning alone, gum surgery may be recommended. These may include open flap scaling and root planing, regeneration therapy, or gum grafting, depending on your individual clinical situation.
If you’ve noticed signs of gum recession or sensitivity, an early dental assessment can help determine the most appropriate treatment and prevent further damage. Our dentists at Thomson Medical will offer clear guidance and personalised care to support your oral health. Request an appointment today.
Our dentists in Singapore
Loading...
What is gum grafting?
A gum graft (also known as a gingival graft or periodontal plastic surgery) refers to the treatment of receding gums, restoring gum tissue and providing protection to the teeth while enhancing the appearance of a smile.
Why do I need gum grafts?
A dentist usually suggests gum grafting when your gum tissue has receded and can no longer protect your teeth properly. Beyond improving appearance, this procedure plays an important role in maintaining your long-term oral health.
This procedure may be recommended to help:
Protect your exposed roots from decay and damage
Cover any exposed roots to reduce your tooth sensitivity
Enhance the appearance of your gum line and smile
Prevent further gum recession, tooth loss and bone loss
What are the potential risks and complications?
As with any surgical procedure, gum grafting carries some potential risks. Most are temporary and manageable, especially when the procedure is performed by an experienced dentist and followed by proper aftercare.
Bleeding and swelling:
This risk is common initially but should subside in time.
Infection:
Infections are rare but possible.
Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help with this.
Graft failure:
In the case of the tissue not integrating properly, a second procedure might be needed.
Sensitivity:
You may feel temporarily sensitive at the graft and donor site.
While these risks may sound concerning, severe complications are uncommon. Most people heal well and experience a smooth recovery.
What are the types of gum graft procedures?
There are many types of gum grafting procedures, and the most suitable option depends on the extent of gum recession, the condition of the surrounding tissues, and your individual oral health needs.
Here are some common types of gum grafting procedures that your dentist may discuss with you.
Connective tissue graft
Commonly used for treating root exposure, a flap is created in the roof of the mouth (palate). Tissue from beneath this flap, known as subepithelial connective tissue, is then removed and stitched to the gum tissue around the exposed root.
Free gingival graft
In this procedure, tissue is directly taken from the outer layer of the palate and attached to the receding gum area. This helps those with thin gums who need additional tissue to prevent further recession
Pedicle graft
This involves grafting gum tissue from tissue closer to the tooth that needs repair. A flap (pedicle) is then halfway cut so one edge is still attached as the gum is pulled over or down to cover the exposed root. Pedicle grafts are suitable for patients with plenty of gum tissue near the affected tooth.
What is the overview of the procedure?
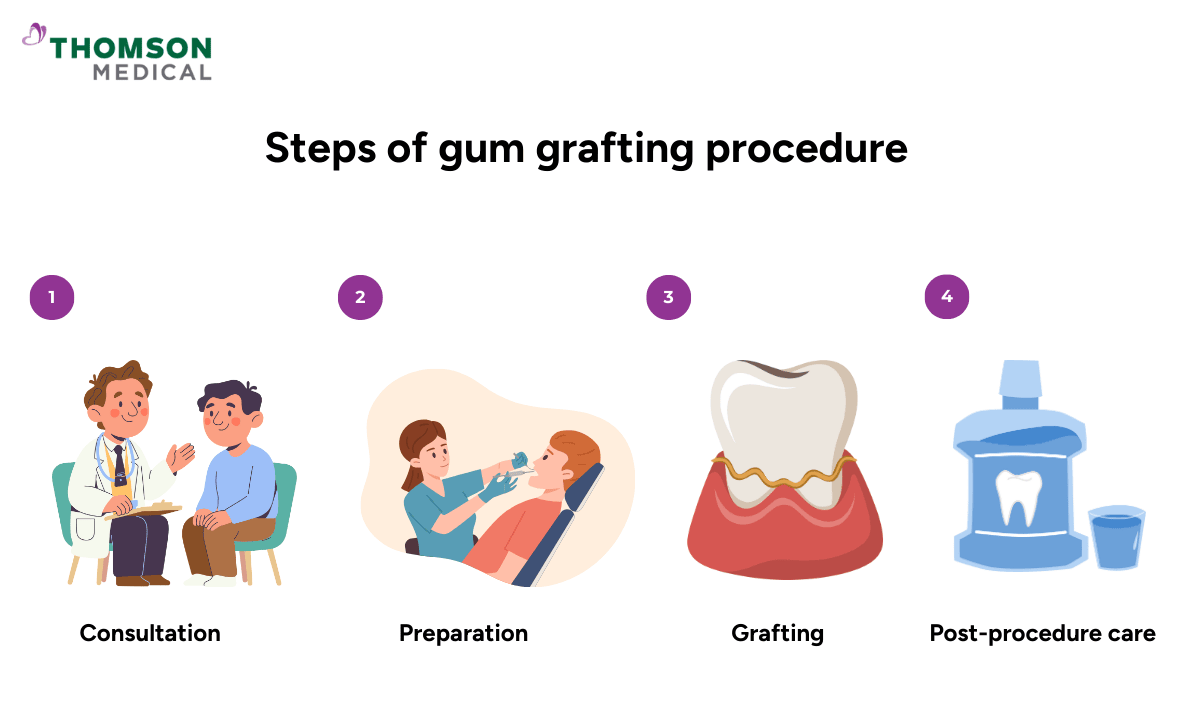
An overview of the gum grafting process may help you set clear expectations for treatment and recovery. While the exact steps may vary depending on the grafting technique used, the procedure usually follows a structured sequence.
Consultation
Your dentist or periodontist may discuss your medical history and examine the extent of gum recession to determine the appropriate type of graft.
Preparation
Usually, local anaesthesia is used to numb the treatment area and sedation may sometimes be used for patient comfort.
Grafting
Tissue is harvested from the palate or nearby gum area and then grafted to the site of recession before then being secured with sutures.
Post-procedure care
Your dentist would prescribe pain relievers and antibiotics to prevent infection, administer a special mouthwash to control plaque and bacteria and provide instructions on maintaining oral hygiene to avoid disturbing the graft site.
Recovery and aftercare
Recovery after a gum graft surgery is usually straightforward when aftercare instructions are followed carefully.
In the initial phase, healing typically takes around one to two weeks, with full recovery expected within four to six weeks.
During the early days, your dentist may recommend the following to support healing:
Diet:
Eat soft, cool food immediately after the procedure
Avoid spicy, hot, or crunchy foods that might irritate the graft site
Oral hygiene:
Try to avoid the graft site when gently flossing and brushing with soft-bristled toothbrush
Use the antimicrobial mouthwash prescribed to you
Follow-up visits:
Attend scheduled check-ups to ensure proper healing
Maintaining a good oral care routine and regular dental visits are key to preserving the successful results of the graft.
Gum grafting is a proven approach for managing gum recession, and when carried out by experienced dental professionals, it can achieve reliable, long-term results. At Thomson Medical, our dentists perform this procedure with careful planning and attention to patient comfort. Request an appointment to discuss your concerns in detail and gain a clear understanding of the procedure before making any decisions.
FAQ
Do electric toothbrushes cause receding gums?
Electric toothbrushes are considered safe and effective to protect your oral health when used correctly. Gum recession is more often linked to brushing too hard or using the wrong technique.
Can receding gums grow back?
No, gum tissue does not grow back naturally once it has receded. However, progression can be slowed, and treatments such as gum grafting can restore coverage and protection.
What do receding gums look like?
Receding gums may make teeth appear longer, expose the tooth roots, or create small gaps near the gumline. Sensitivity is also common.
How painful is gum grafting?
Most people report mild to moderate discomfort rather than significant pain. The procedure is performed under local anaesthesia, and postoperative discomfort is usually manageable with medication.
How long does a gum graft last?
With good oral hygiene and regular dental care, a gum graft can last many years and usually provides long-term stability.
How much is gum grafting in Singapore?
The cost of gum grafting in Singapore varies depending on the extent of recession and the type of graft required. During a consultation, your dentist will assess your dental condition and provide an accurate estimate for gum grafting.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and advice based on your unique situation, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
_1440x810.png%3Fbranch%3Dprod&w=3840&q=75)