If you've noticed unusual spots, bumps, or rashes on your child's skin, you're probably feeling concerned and looking for answers. It's completely natural to worry when something doesn't look quite right, especially when your little one is uncomfortable or self-conscious about their skin.
Fortunately, skin infections are very common in children – most kids will experience at least one type during their early years. Understanding what you're looking at and knowing when to seek help can make all the difference in keeping your child comfortable and healthy.
What are skin infections in children?
A skin infection happens when tiny organisms – like bacteria, viruses, or fungi – find their way onto or into your child's skin. Kids are more likely to get these infections because their immune systems are still developing and they are often around other kids. Small scratches, insect bites, or dry skin patches can create opportunities for these organisms to settle in, but most infections respond well to treatment.
Common skin infections in children
Children's skin is delicate and still developing its natural defences, which means infections can happen even with the best care. Understanding what these infections look like and how they behave can help you respond calmly and effectively when they appear in your child’s skin.
Viral warts in children
Viral warts are one of the most common skin concerns in children. Human papillomavirus (HPV) causes these small, rough bumps, which are completely different from the strains you might have heard about in adult health contexts. The HPV types that cause childhood warts are harmless and only affect the skin's surface.
Your child can pick up the virus from swimming pools, sharing towels, or touching another child who has warts. While warts are usually harmless, they can spread to other parts of your child's body if picked or scratched.
Types of warts and where they appear
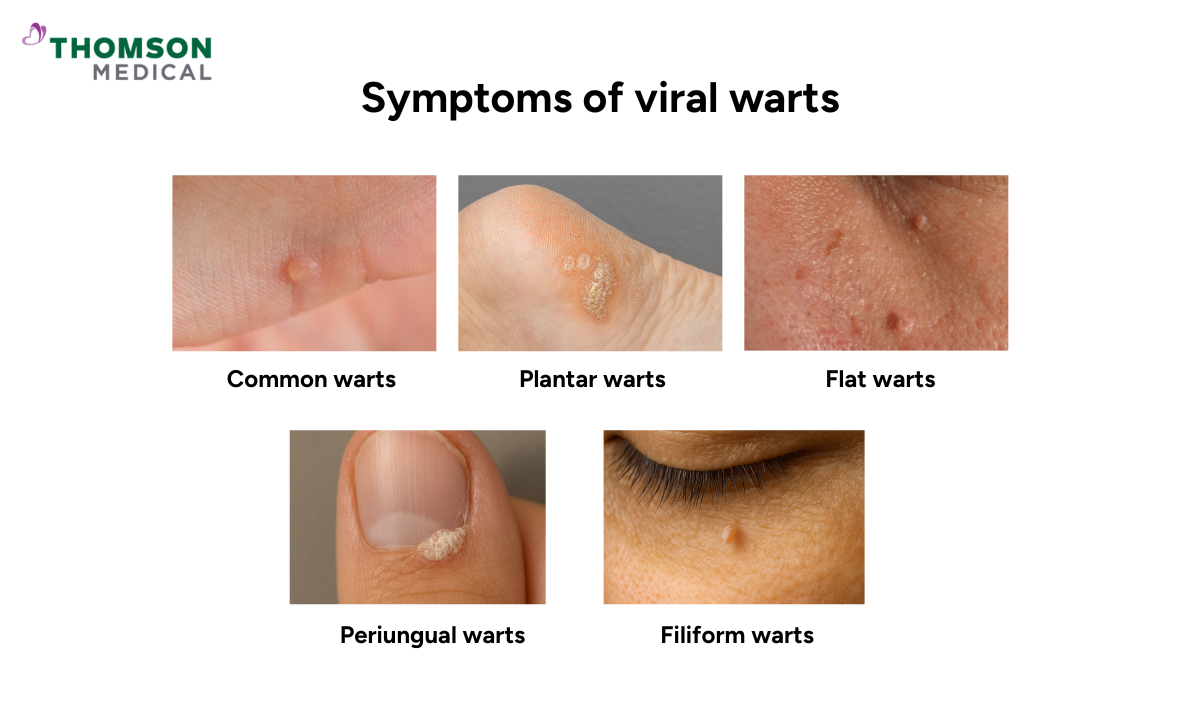
Warts can show up in different forms depending on where they grow on your child's body. The main types are:
Common warts, which show up as rough, raised bumps on fingers, hands, knees, or elbows, often with tiny black dots inside
Plantar warts, which grow on the soles of the feet and can feel like stepping on a pebble when walking
Flat warts, which are smoother and smaller, often appearing in groups on the face, arms, or legs
Filiform warts, which look like tiny threads around the mouth, nose, or eyes
Periungual warts, which appear around or under fingernails and toenails and can cause discomfort
If your child has warts, gently remind them not to pick or scratch, as this can spread the virus. Keep the warts covered with a plaster if your child has trouble leaving them alone.
Fungal infections in children (ringworm)
.png?branch=production)
Despite its name, ringworm has nothing to do with worms. It's a fungal infection that creates circular, ring-like rashes on your child's skin. If you've spotted red, scaly patches that look like rings, you're likely dealing with ringworm.
Children can pick it up from direct contact with an infected person, from touching contaminated objects like towels, or even from pets. It's highly contagious but treatable, so try not to panic if your child has it.
Different types of ringworm
Ringworm can appear on different parts of your child's skin, such as:
Ringworm of the body, which appears as circular, red patches on the torso, arms, or legs with raised, scaly edges and a clearer centre
Ringworm of the scalp, which shows up as scaly patches, broken hair, or bald spots on the scalp, particularly common in young children
Athlete's foot, which causes red, cracked, or peeling skin between the toes or on the soles
Jock itch, which creates red, itchy rashes in the groin area that can spread to the inner thighs
Preventing ringworm from spreading
Once your child has ringworm, it's important to prevent it from spreading to other parts of their body or to family members. Consider taking these steps:
Keep your child’s infected area clean and dry
Wash your child’s hands after touching the affected area
Avoid sharing towels, clothing, hairbrushes, or hats until the infection clears
Make sure your child showers after sports and doesn't share equipment
Keep your child's fingernails trimmed to prevent spreading through scratching
Impetigo in children
Impetigo is a bacterial skin infection that's particularly common in young children. It happens when bacteria enter your child's skin through a cut, scrape, insect bite, or even irritated skin from conditions like eczema.
Even though impetigo is highly contagious, it responds well to treatment, so catching it early makes a big difference. While it most commonly affects children aged two to five, it can occur at any age.
What impetigo looks like
Impetigo usually starts as red sores that quickly burst and develop honey-coloured or yellowish-brown crusts. These sores usually appear around your child's nose and mouth but can spread through scratching.
There are two main types of impetigo:
Non-bullous impetigo, which show up as small blisters that burst and form crusty scabs
Bullous impetigo, which appears as fluid-filled blisters that last longer before bursting
Treating impetigo effectively
If you discover that your child has impetigo, it’s completely normal to feel worried. Luckily, this condition responds well to treatment, though you will need to see a doctor for the right medication. Your doctor will usually prescribe an antibiotic cream for mild cases or oral antibiotics if the infection has spread to multiple areas.
While your child is being treated, these simple steps will help the healing process:
Gently wash your child’s affected area with soap and water
Apply the prescribed medication as directed
Cover the sores with gauze or a plaster to prevent spreading
Keep your child home from school until they've been on antibiotics for at least 24 hours
The positive news is that most children start feeling better within a few days of starting treatment, and the sores often begin to heal quickly.
If you suspect your child has impetigo or notice honey-coloured crusts forming around sores, schedule an appointment with Thomson Specialist Skin Centre. Early treatment can prevent the infection from spreading and help your child recover more quickly.
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD)
.png?branch=production)
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a viral infection that's extremely common among young children in Singapore. If your child gets it, try not to worry – while it can be uncomfortable, it's usually mild and clears up on its own within a week or 10 days.
HFMD spreads easily through close contact, saliva, or contaminated surfaces. Children under five are most vulnerable, though older children can catch it too.
HFMD symptoms to watch for
HFMD often starts with symptoms that might look like a common cold. You'll usually notice:
Fever, often the first sign
Sore throat that makes eating uncomfortable
Loss of appetite and general tiredness
A day or two later, the telltale signs appear, such as:
Painful red spots or blisters in your child's mouth, on the tongue, gums, or inside the cheeks. These can make drinking and eating quite difficult.
A rash of flat red spots or blisters on the palms, soles of the feet, and sometimes on the buttocks. Unlike other rashes, these usually don't itch.
The mouth sores are often the hardest part for little ones. If your child is refusing to eat or drink because it hurts, offer cool, soft foods and plenty of fluids to keep them hydrated. Lastly, try to avoid anything acidic or spicy that might sting the sores.
Most children recover without complications, but watch for signs of dehydration like reduced urination, dry lips, or unusual sleepiness. If you notice these, it’s better to contact your doctor.
If your child is showing signs of dehydration or the symptoms are making them very uncomfortable, request an appointment with Thomson Specialist Skin Centre. Our doctors can assess your child's condition and provide guidance on managing their symptoms effectively.
Molluscum contagiosum in children
.png?branch=production)
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes small, raised bumps on your child's skin. While the bumps might look concerning, this infection is harmless and common in children.
The bumps are usually flesh-coloured, white, or pink, with a distinctive dimple in the centre. They appear most commonly on the face, neck, arms, and hands. The infection spreads through direct skin contact or touching contaminated objects.
What to expect and how to manage it
Molluscum contagiosum takes time to clear, sometimes months or even up to two years, but it will go away on its own. Fortunately, the bumps don't usually hurt or itch.
Treatment isn't always necessary, but your doctor can talk through removal options if the bumps are bothering your child. In the meantime, you can help prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum by:
Remind your child not to pick or scratch the bumps
Keep affected areas covered during swimming or contact sports
Avoid sharing towels or clothing
Scabies in children
If your child is scratching intensely at night, scabies might be the cause. It's caused by microscopic mites that burrow into the skin, and while the thought can feel unsettling, it's a common childhood condition that responds well to treatment.
What scabies looks like

The itching with scabies is often worse at night and can be quite distressing for little ones. Look for these signs:
Small red bumps or blisters in skin folds
Common areas include between fingers, wrists, elbows, armpits, waistline, or nappy area in babies
Thin, irregular lines on the skin where mites have burrowed
How it spreads and what to do
Scabies spreads through close, prolonged skin-to-skin contact, which is why it often affects multiple family members or children in daycare.
Treatment requires prescription medication applied to the entire body, and everyone in the household usually needs treatment at the same time. You'll also need to wash bedding, towels, and clothing in hot water and vacuum furniture thoroughly.
The itching may persist for a few weeks after treatment as your child's skin heals. If it happens, try not to worry – this is normal and doesn't mean the treatment hasn't worked.
Our skin specialist in SIngapore
Loading...
When to see a doctor for your child's skin infection
As a parent, it's natural to wonder whether a rash or infection needs medical attention or if it'll clear up on its own. Here are the signs that show it's time for your child to see a doctor:
The infection is spreading quickly or becoming more painful
Your child develops a fever
There's pus, oozing, or red streaks spreading from the infection
The rash hasn't improved after a few days of home care
Your child seems unwell, unusually tired, or isn't eating normally
For younger children and babies, it's generally better to be cautious. If you feel something isn't right, trust your instincts and get them checked. Some infections require prescription treatment and won't improve without it.
If your child is showing any of these signs or you're concerned about a skin infection, schedule an appointment with Thomson Specialist Skin Centre. Our doctors can assess your child's condition and provide the right treatment to help them feel comfortable again.
FAQ
Are skin infections in children contagious?
Many skin infections in children are contagious, including:
Impetigo
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD)
Molluscum contagiosum
Ringworm
Scabies
Warts (through direct contact)
Good hygiene practices like regular handwashing and not sharing personal items can help reduce transmission.
Do skin infections require my child to stay home from school or daycare?
You may need to keep your child home if the skin infection is contagious, spreading, or making them uncomfortable. If there is fever, open sores, increasing redness, or drainage that can’t be covered, it’s safer for them to rest at home.
Once treatment has started and the infection is no longer spreading – or can be properly covered – they can usually return to school or daycare. If you're unsure, checking with your child’s doctor or the school’s health guidelines can help.
Can skin infections go away on their own without treatment?
Some mild infections may clear up on their own, but many require treatment to heal properly and prevent spreading. Bacterial infections like impetigo need antibiotics, whereas scabies requires prescription medication. It's best to have a doctor assess the infection to determine if treatment is needed.
How long does it take for skin infections to heal with treatment?
Healing time depends on the type and severity of the infection. Many mild skin infections start improving within a few days of treatment and clear up in about one to two weeks. More stubborn or deeper infections may take longer.
If your child’s symptoms aren’t getting better as expected or seem to worsen, it’s best to check in with a healthcare provider for further guidance.
What's the best way to prevent my child from getting skin infections?
Wash hands regularly, as this is the most effective prevention method
Keep your child's skin clean and moisturised
Treat cuts and scratches promptly
Avoid sharing towels, clothing, or personal items
Teach your child not to touch or scratch existing infections
Why does my child keep getting the same skin infection repeatedly?
Recurring infections can happen for several reasons. The original infection may not have been fully treated, or your child might be re-exposed to the source. Children with skin conditions like eczema may have more entry points for infections. Speak with your doctor if the infection keeps returning.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice based on your unique situation, please consult a specialist at Thomson Specialist Skin Centre. Schedule an appointment with Thomson Specialist Skin Centre today.
Dr Tan Hiok Hee
Dermatology (Skin)
Thomson Specialist Skin Centre (Novena Specialist Center)
English, Mandarin
.png%3Fbranch%3Dprod&w=640&q=75)
.png%3Fbranch%3Dprod&w=3840&q=75)