Couples struggling to conceive often ask which is better between in vitro fertilisation (IVF) vs. intrauterine insemination (IUI)? While both treatments aim to increase the chances of conception, these procedures differ in terms of their execution, cost, success rate, and suitability to address your fertility issues.
Understanding the difference between these two fertility treatments helps you make an informed decision, whether you just started your fertility journey or are already considering the next one.
What is IVF?
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a type of assisted reproductive technology (ART) where sperm and eggs are fertilised outside of your body. IVF is a complex process that involves retrieving eggs from your ovaries and manually fertilising them with sperm in the lab.
Afterwards, a procedure is performed to transfer the fertilised egg (embryo) back into your womb, where it can develop further. A complete IVF cycle usually lasts 4 to 6 weeks but can be longer if necessary.
When should I choose IVF?
Artificial insemination is usually recommended for couples with severe infertility. If you have had 3 or 4 failed IUIs, failed to conceive after having regular unprotected sex for more than 1 year and are a woman older than 35 years old, IVF is a suitable option.
In addition to the reasons above, here are some factors that you can consider if you and your partner want to use IVF as a treatment option, among others:
Having severe male-factor infertility, such as extremely low sperm count and motility.
Wanting to preserve fertility before undergoing treatment such as radiation or chemotherapy that can harm fertility.
There is a high risk of inheriting a genetic condition.
Severe endometriosis, which can lead to complications such as blood in urine or faeces, significant pain during bowel movements, and shortness of breath or chest pain.
A blocked or damaged fallopian tube prevents sperm from fertilising an egg in the tube and obstructs the passage of a fertilised egg to the uterus.
A tumour in the uterus, known as uterine fibroids, causes the fertilised egg to have difficulty attaching to the uterine lining.
Unexplained infertility, which occurs when the healthcare providers are unable to determine the cause of your infertility, even after several IUI attempts.
How is IVF performed?
An IVF procedure usually follows these procedure steps, which include:
Ovary stimulation
IVF treatment begins with the administration of fertility drugs designed to increase the number of eggs produced from the usual single egg released each month. Multiple eggs allow the doctor to select the eggs that have the best chance of success.
This process can last between 1 and 2 weeks.
Egg retrieval
After the final shot of fertility drugs and before your natural ovulation, the eggs are retrieved from the ovaries using a procedure called transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration.
During this procedure, an ultrasound device is inserted into the vagina to direct a thin needle toward the ovaries to retrieve the eggs from the follicles. This process usually lasts 15 to 30 minutes, and anaesthesia is administered to reduce pain.
Sperm preparation
Before fertilisation can begin, quality sperm is collected, usually during the egg retrieval process or from a frozen state.
Fertilisation
There are two common ways to fertilise eggs with sperm.
The first one is conventional insemination, where healthy sperm and mature eggs are mixed and kept in a controlled environment called an incubator.
The second procedure involves injecting a single sperm directly into the mature egg, known as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). But this procedure is reserved only if there is a semen quality issue.
Following fertilisation, the eggs begin to divide and develop into embryos. These embryos are monitored in a laboratory setting for around 2 to 5 days.
Embryo transfer
Several days after fertilisation, the healthy embryo is placed back inside the uterine cavity using a thin, flexible tube (catheter). A successful pregnancy occurs when this embryo implants itself into the uterine wall.
After the procedure
After the embryo transfer, you can get back to your usual daily routine. Your ovaries may still be enlarged, so vigorous activities like sexual intercourse are not advised.
Other side effects may include breast tenderness due to high oestrogen levels, mild bloating and cramping, and constipation.
After the embryo is placed in your womb, you need to wait at least two weeks before taking a pregnancy test to determine a successful pregnancy.
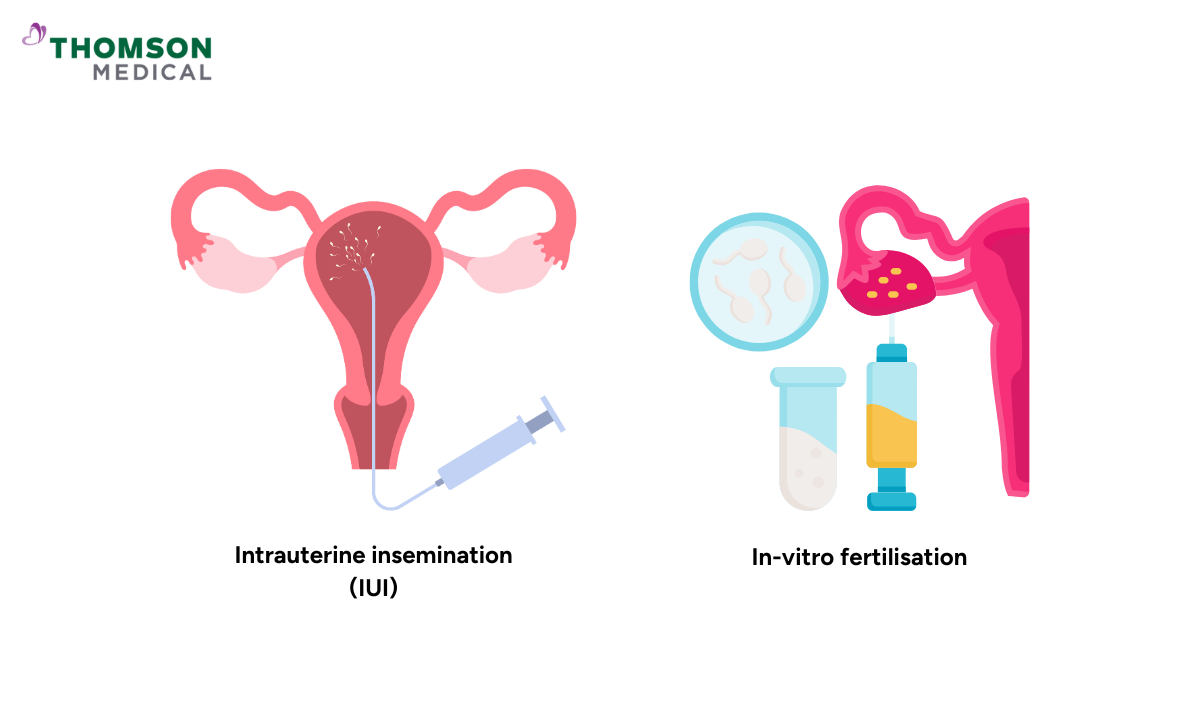
What is IUI?
An intrauterine insemination (IUI) is another common fertility treatment that places sperm directly into the womb during your fertile period. The technique is a less invasive procedure that reduces the distance sperm have to travel and gives them a better chance of reaching your eggs.
IUI is often suggested as the first treatment for couples who can't get pregnant for no clear reason, have mild fertility problems, or have problems with their cervix. This is because the sperm has been "washed" in the lab to concentrate the healthiest and most mobile sperm.
When can I choose IUI?
An IUI treatment is a simpler and less invasive procedure with a reasonable success rate, making it a good first option for fertility treatment. Here are some factors that you can consider if you and your partner want to use this artificial insemination as a treatment option:
Experiencing mild male-factor infertility, which is characterised by reduced sperm count, abnormally shaped sperm, and some motility issues.
Unexplained infertility, where the healthcare providers can't find the cause for your infertility even after a thorough evaluation.
Unsuccessful conception after regular unprotected sex for 1 year
Experiencing a thick cervical mucus issue, which can hinder sperm movement from the vagina to the womb.
Endometriosis, which causes tissue that's like the lining of the uterus to grow outside of it.
Ovulation problems, where there's a decline in fertility because of irregular periods, a reduced number of released eggs, or anovulation (absence of ovulation).
Semen allergy, which is an allergy triggered by the proteins in semen, causing a burning feeling and swelling where the semen touches the skin.
Erectile dysfunction (impotence), which causes the penis to be unable to get up or keep an erection firm enough during the duration of intercourse.
How is IUI performed?
IUI is a relatively simple and straightforward procedure that usually follows these steps:
Ovulation tracking
The first step of the IUI procedure is monitoring your menstrual cycle to determine your fertile window. A fertility specialist will also help track the growth of the eggs in the ovaries with ultrasound exams and blood tests.
To help this process, you can also monitor your natural cycle by yourself by tracking your body temperature, observing changes in your cervical mucus, and using fertility tracking apps.
Sperm sample collection
Before the insemination process begins, your partner will need to provide a fresh semen sample.
This sample then undergoes a "sperm washing" procedure, which separates the sperm from the seminal fluid and isolates the healthiest and most motile sperm for the insemination process.
For the best results, it’s advisable to refrain from ejaculation for 1-3 days prior to the collection.
Insemination
At the time of ovulation, the prepared sperm is injected directly into the uterine cavity using a thin, flexible tube (catheter). IUI shortens the distance for the sperm to reach the egg resting in the fallopian tube and increases the chances of pregnancy.
Post-procedure
After the IUI procedure, you might be advised to take a short rest before resuming your normal activities, especially strenuous exercise. There are some mild symptoms that you can experience after IUI, such as mild cramping or light spotting for one or two days.
To determine a successful pregnancy, you'll need to wait at least two weeks after the IUI procedure before taking a pregnancy test.
If you are unsure which fertility treatment is suitable for your condition, request an appointment with Thomson Fertility Centre. Our fertility specialists can help provide a tailored recommendation on which treatment is suitable for you based on your fertility condition.
IVF and IUI specialists
Loading...
Differences between IVF and IUI
Even though both treatments aim to help couples with infertility challenges and increase the likelihood of conception, there are differences between them. To make an informed decision, here are the differences between the two treatments in terms of invasiveness, cost, and suitability for different fertility issues.
Feature | In-vitro fertilisation (IVF) | Intrauterine insemination (IUI) |
Procedure implementation | The process is carried out in a laboratory to facilitate the fertilisation of the egg by the sperm. | The process is carried out inside the womb to allow for natural fertilisation within the fallopian tubes. |
Invasiveness | More invasive, to extract the egg from the ovaries, a thin needle guided by an ultrasound is used. Additionally, a catheter is required to insert the embryo into the womb. | The procedure is less invasive, as it only involves inserting a catheter during insemination. |
Chances of success | An IVF procedure has a success rate around 50% for women under 35. This number decreases with age, to around 20% for women if they're 40 years old. | The rates per cycle for the IUI procedure are around 20% if you're younger than 35 years old. This rate diminishes to around 5% if you're over 40. |
Cost | An IVF procedure is more expensive due to lab procedures. Medisave or government co-funding can reduce the cost to around SGD 15,000 per menstrual cycle. | An IUI procedure is more comfortable, costing around SGD 1,500 in public hospitals. The procedure can cost between SGD 2,000 and 3,000 if performed in private clinics. |
Fertility medication | The stimulation of the ovary is required to increase the number of eggs the ovaries produce. | It can be used to help the release of the egg from your ovaries (ovulation); this procedure is called superovulatory IUI (SO-IUI). |
Number of cycles required | Pregnancy rate can be higher in the first two cycles compared to IUI | 3-4 cycles are usually needed before moving into IVF. |
To determine which fertility treatment works best for you, it is important to have a thorough consultation with a fertility specialist. Request a consultation with our fertility specialist at the Thomson Fertility Centre for personalised recommendations.
FAQ
What is the difference between IUI and IVF?
At IUI, fertilisation occurs naturally in your uterus. Because in this fertility treatment, your partner's prepared sperm is placed directly into the womb using a catheter.
Meanwhile, in IVF, fertilisation is performed by a healthcare professional in the lab. It's also a more complex process, which involved multiple steps in a laboratory setting before transferring the resulting embryo back into the womb.
Which one is better, IUI or IVF?
IVF may appear to have a higher success rate for infertility issues, but the most appropriate treatment should be based on your infertility circumstances. In addition, the cost of IVF is higher than that of IUI, and it is a more invasive fertility treatment.
What's the difference between insemination and fertilisation?
Insemination and fertilisation are two different processes during conception. Insemination refers to the deposition of sperm in the vagina, while fertilisation is the biological process where the sperm and egg combine to form an embryo.
Should I skip IUI and go straight to IVF?
You may go straight to IVF if you've undergone 3-4 IUI cycles without conceiving or if your female partner is older than 35 years old. But you need to remember that the decision to pursue IUI or move directly to IVF should be made in careful consultation with your fertility specialist.
What are the disadvantages of IUI?
While IUI is a more straightforward and less invasive procedure, it does come with some drawbacks. Here are a few disadvantages associated with this fertility treatment:
A small risk of pelvic infection post-IUI.
Multiple treatments may be necessary before successful fertilisation.
Lower success rates compared to an IVF procedure, with approximately 20% success per cycle for women under 35 years old.
The use of hormones in the SO-IUI procedure can lead to the development of 3–4 eggs, increasing the chances of multiple pregnancies such as twins or triplets.
Can you pick gender with IUI?
No, you can't choose a gender with IUI because this fertility treatment simply places prepared sperm closer to the egg to increase the chances of natural fertilisation. The sperm that fertilises the egg naturally determines its gender, and IUI cannot control this process.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice, request an appointment at Thomson Fertility Centre.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Fertility Centre
- Paragon: +65 6252 7766
