What is an ovarian cysts?
An ovarian cysts is a condition where sacs filled with fluid or semi-solid material develop within one or both ovaries. These cysts are usually painless and noncancerous (benign), but occasionally they might cause complications such as ovarian torsion or rupture.
You may not be aware of this condition unless you consult a healthcare provider for a pelvic ultrasound examination. You might think that the symptoms you feel are related to menstrual or weight issues.
This happened to one of my patients when she thought that she had gained weight with a visible bulge when lying down. She also mentioned experiencing mild abdominal cramps over several months, which she thought was indigestion.
But when she made the decision to see me, an abdominal examination revealed a cyst the size of a grapefruit.
What causes ovarian cysts?
This condition can be caused by hormonal changes during your menstrual cycle and can be a sign that your ovaries are working as they should. These cysts usually shrink on their own, usually within 60 days.
So most cysts are harmless, but sometimes there are other causes unrelated to the menstrual cycle that can cause this condition, such as:
1) Abnormal cell reproduction
Abnormal cell reproduction can cause dermoid cysts or cystadenomas to form.
2) Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when tissue that’s similar to the inner lining of the uterus grows outside of it, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the tissue lining the pelvis.
When attached to the ovaries, this tissue can form endometriomas (blood-filled cysts).
3) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that causes the ovaries to develop many small fluid-filled sacs (cysts) on the outer edge of the ovary.
This condition can happen when your body doesn’t make enough hormones needed to cause ovulation.
4) Pregnancy
During pregnancy, corpus luteum cysts can develop from the follicle that releases an egg. These cysts typically resolve as the pregnancy progresses but may occasionally grow larger.
Risk factors
In addition to the causes mentioned above, there are other factors that may increase the risk of ovarian cysts, such as:
Hormonal imbalances
A hormonal imbalance of estrogen and progesterone can affect the ovulation cycle, which can lead to cyst formation.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
This condition is an infection that usually occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from the vagina to the ovaries and cause cysts to grow.
Previous ovarian cysts
If you've had a history of ovarian cysts, you're likely to develop this condition again in the future.
Types of ovarian cysts
Based on the causes above, there are a few types of cysts that may develop, including:
Functional cysts
This type of cyst occurs naturally when your ovaries grow small sacs called follicles each month. This follicle will break open to release an egg when it's time for you to ovulate. There are two types of functional cysts:
Follicular cysts
Due to the menstrual cycle, a follicle will grow and develop an egg cell inside. When the egg has matured, the follicle breaks open and releases it during ovulation.
If the follicle doesn’t open as it should, it can be filled with fluid and form a cyst.
Corpus luteum
After the follicle releases an egg, it normally shrinks and begins creating estrogen and progesterone hormones. The empty follicle is called the corpus luteum, if conception doesn’t take place, the corpus luteum dissolves.
But sometimes, instead of breaking down, it fills with fluid and forms a cyst.
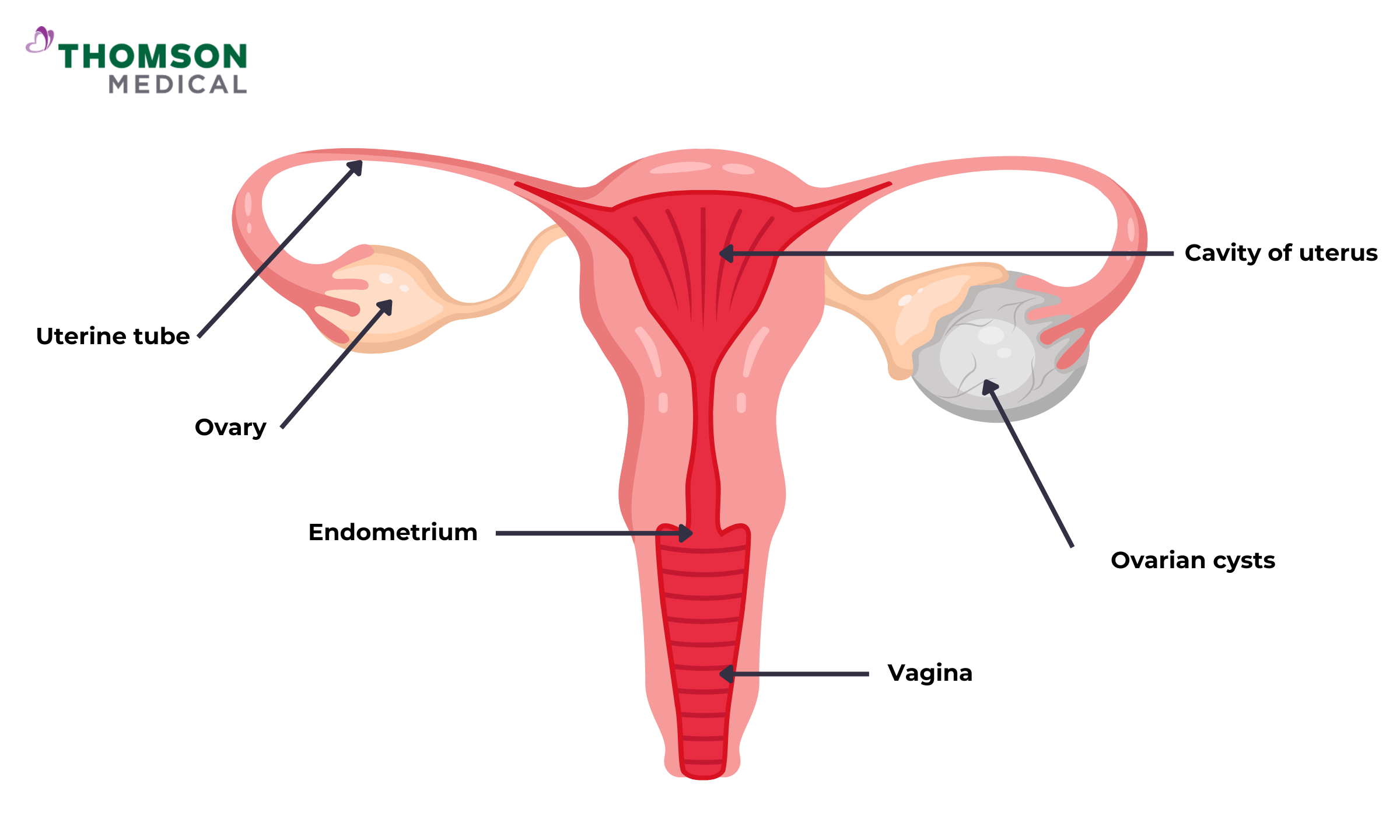
Other cysts
This type of cyst means that they don't form as part of the menstrual cycle. These cysts aren’t always a disease, but you need to see a healthcare provider to monitor it to ensure that they don’t cause any other health problems.
Other types of ovarian cysts include:
Cystadenomas
This type of cyst develops from cells on the surface of the ovary, it’s filled with thin, watery, or thick mucous material and can grow larger than other types of ovarian cysts.
Dermoid cyst (teratoma)
Dermoid cysts (teratomas) are one of the most common types of cysts found in females between the ages of 20 and 40. A dermoid cyst comes from reproductive cells that make eggs in the ovary (germ cells).
The cysts can contain tissue, such as skin, hair, teeth, or fat. While this sac is usually noncancerous, sometimes it can be cancerous.
Endometrioma
People with endometriosis can develop a type of ovarian cyst called an endometrioma, or “chocolate cyst”, where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows in the abdomen or pelvis, forming a cyst on the ovary (which can be filled with blood).
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the ovaries or fallopian tubes grow and multiply out of control. Ovarian cancer cysts are usually filled with solid masses of cancer cells.
This condition can happen at any age, but a cyst that develops after menopause is more likely to be cancerous.
Ovarian cysts symptoms
Usually, ovarian cysts do not cause symptoms. However, a large cyst may cause dull aching pain or a heavy sensation in the pelvic area.
Some of the symptoms that might happen from an ovarian cyst include:
Abdominal pain in the area below your belly button that may come and go
Bloating in the lower belly
Nausea, fever, and vomiting
Pain during sex (dyspareunia)
Painful and irregular periods
Trouble pooping or needing to pee frequently
If you are experiencing multiple symptoms listed above that have persisted over time, request a consultation with specialists at Thomson Women's Clinic. Our healthcare professionals are ready to provide you with a reliable assessment and a customised treatment plan.
How are ovarian cysts diagnosed?
To diagnose this condition, I usually begin by reviewing your medical history and performing a pelvic examination to detect any lumps or changes in the pelvis. After that, a pregnancy test might be done to rule out the possibility of pregnancy.
To diagnose and help determine the type of condition, other tests may also be performed, including:
Ultrasound
This type of imaging test uses sound waves to create images of your pelvic organs. It can detect the cyst's size, locations, and whether they’re filled with fluid filler or solid.
CT scan or MRI
A computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may be performed to produce in-depth images of internal organs and look for any evidence of ovarian cancer.
Laparoscopy
This minimally invasive procedure involves a camera being inserted through a small cut in the abdomen to view reproductive organs and the pelvic cavity and look for any cysts.
Blood tests
To check if there’s any ovarian cancer, a cancer antigen 125 (CA125) test or other blood tests may be performed. Blood levels of a protein called a cancer antigen are often elevated in ovarian cancer.

Nonsurgical treatment options for ovarian cysts
Treatment for this condition will depend on the type and size of the sacs, the symptoms you're experiencing, and whether you're in menopause or still in the normal menstrual cycle.
For women with normal menstrual cycles, the cysts will disappear on their own within two months without treatment. But if you have been through menopause, ovarian cysts are less likely to disappear on their own.
To treat this condition, there are non-surgical treatment options available, such as:
Watchful waiting
If the diagnosis shows that the cyst is likely related to your monthly cycle, a wait-and-see approach is recommended.
You will probably have a follow-up ultrasound scan in a few weeks or months to see any changes in the cyst.
Medication
Medications containing hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, might be given to stop ovulation and prevent cysts from developing.
Surgical treatment options for ovarian cysts
If the cyst is large (around 5 to 10 cm), causing sharp pain, or if there are concerns that the cyst could be cancerous, a surgical procedure is needed to remove it.
The type of surgery recommended will depend on several factors, including the cyst's size, appearance, and your health conditions. There are two surgical procedures that might be performed:
1) Laparoscopic surgery (keyhole surgery)
During this minimally invasive surgery (laparoscopy), the surgeon will make small cuts in your abdomen. After that, a thin tube with a camera (laparoscope) and surgical instruments are inserted.
This procedure can be conducted as a cystectomy, which involves removing only the cyst while preserving the ovary. Alternatively, it may be performed as an oophorectomy, where the entire ovary and the cysts are both removed.
2) Laparotomy
This traditional surgical approach involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the cyst. This procedure is reserved for larger cysts or when there is a suspicion that the cyst could be cancerous.
During a laparotomy, if the ovary cannot be saved, an oophorectomy may be performed, which will remove one or both ovaries depending on the situation.
For personalised advice regarding which treatment type would serve you the best, request a consultation with our gynaecologist from Thomson Women's Clinic.
Possible complications
Although rare, some complications might happen with ovarian cysts, including:
1) Ovarian torsion
Large cysts can cause the ovary to twist, which restricts blood supply and causes severe pain, nausea, and vomiting. If not properly treated, ovarian torsion can harm the ovary and may result in the loss of ovarian tissue.
2) Ovarian cyst rupture
A large cyst may rupture, causing severe pain and internal bleeding. This complication might happen when there's vigorous activity that affects the pelvis, such as vaginal sex.
If left untreated, this complication can increase your risk of an infection and can be life-threatening.
FAQ
What does ovarian cyst pain feel like?
An ovarian cysts may cause a dull ache or a heavy sensation in the pelvic area, particularly below the belly button, with varying intensity. However, in most cases, ovarian cysts don't cause any symptoms and resolve on their own as time passes.
How do I get rid of my ovarian cyst naturally?
A functional cysts, which is a part of your monthly cycle, will naturally disappear on their own within two months without requiring treatment. However, other types of cysts will need proper medical monitoring with regular ultrasound scans to monitor the cyst's size and appearance.
When should I be worried about an ovarian cyst?
If you experience sudden or severe pain, nausea, vomiting, abnormal bleeding, or bloating, seek medical attention immediately. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are important.
What can I do to prevent ovarian cysts?
Currently, there isn’t a known method to prevent ovarian cysts. Regular gynaecological exams, however, can identify cysts early and track their progression.
Is a 4 cm ovarian cyst big?
A cyst is considered "big" if it's around 5 to 10cm in size, so 4cm is still below this threshold and would probably not be classified as a big cyst that requires surgical removal. However, it's important to note that the treatment of ovarian cysts depends on several factors in addition to size, including:
The type of cyst
Your symptoms
Whether you're pre- or post-menopausal
The appearance of the cyst on imaging
For a 4 cm cyst, your doctor might recommend "watchful waiting" with a follow-up pelvic exam to monitor any changes, particularly if you have regular menstrual cycles and the cyst appears to be a functional type.
Can I still get pregnant if I have an ovarian cyst?
Ovarian cysts usually do not affect fertility. However, conditions like hormonal imbalance, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), or endometriosis that cause cysts can affect your ability to conceive. Consult your doctor if you are concerned about fertility.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice, request an appointment at Thomson Women's Clinic today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
Request an AppointmentDr Ryan Lee Wai Kheong
Obstetrics & Gynaecology (O&G)
Thomson Specialists Woodleigh (Women's Health)
English, Mandarin
Great Eastern, Adept, MHC, HSBC and 2 others

