What is Pap smear?
The Pap smear, also known as Pap test or cytology, is a screening procedure used to detect abnormal cellular changes in the cervix, which could indicate the presence of cervical cancer or precancerous conditions.
Pap smear purpose: Why is Pap smear being done?
The primary goal of a Pap smear is to detect cellular abnormalities in the cervix, particularly those caused by persistent high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
This screening is important as they can detect pre-cancerous changes, allowing for timely intervention and preventing the progression to cervical cancer. This preventive measure has contributed significantly to the reduction of cervical cancer incidence and mortality rates.
Pap smear age: When should you get your first Pap smear?
According to the Ministry of Health (MOH), all women who have ever engaged in sexual intercourse should undergo cervical cancer screening starting at the age of 25.
How often do you need a Pap smear?
According to MOH guidelines, women aged 25 to 29 are advised to have a Pap smear every three years. This recommendation does not apply to women with a history of previous abnormal Pap smears who are following up with a gynaecologist.
For women aged 30 and older, they are recommended to get an Human Papillomavirus (HPV) test every five years.
Pap smear procedure: How is pap smear done?
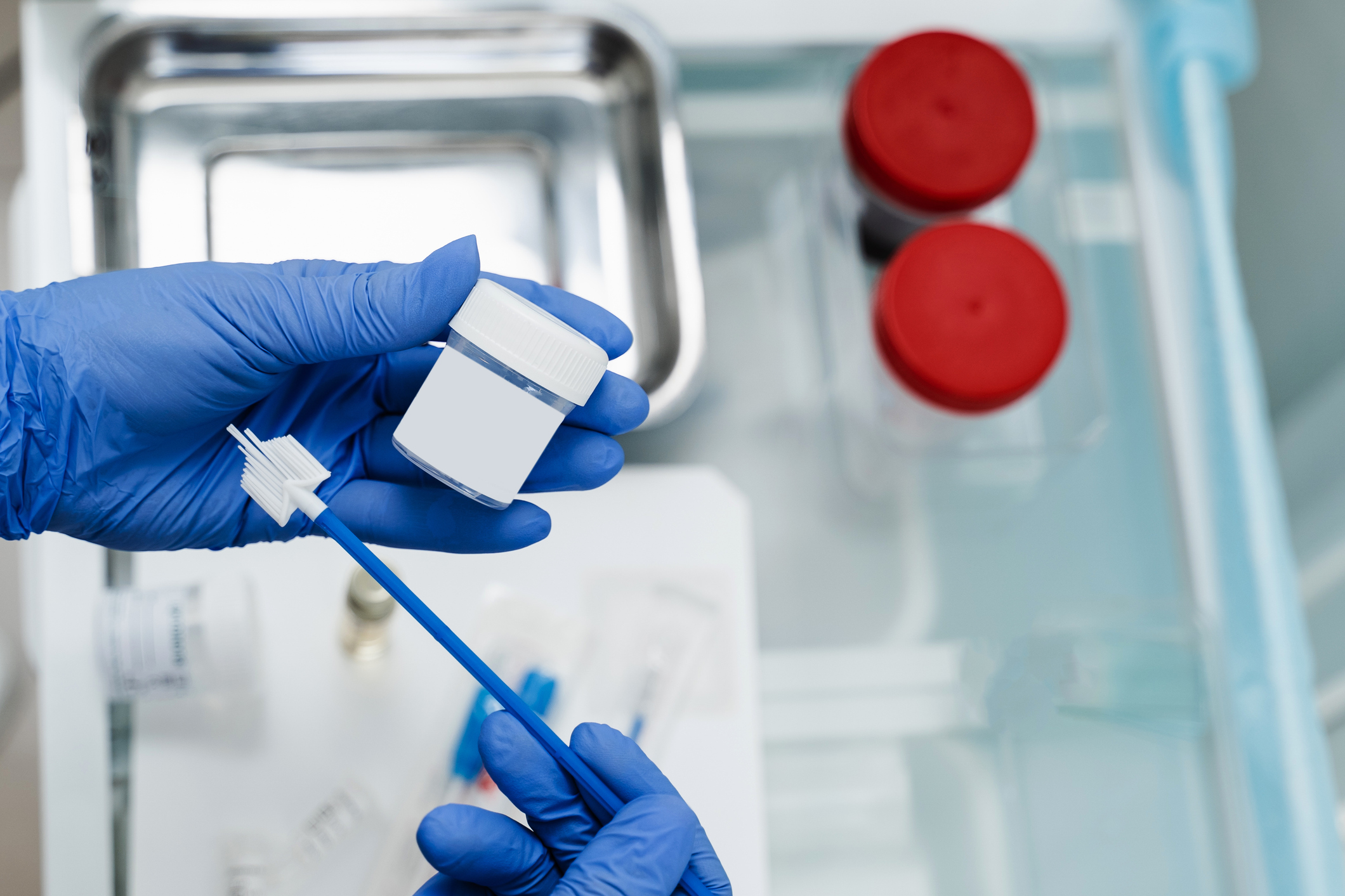
Pap smear involves the following steps:
Positioning: A speculum is gently inserted into your vagina to widen it. Cell collection: Cells are collected from the cervix using a brush or spatula. They will be sent to a lab to identify any abnormalities.
Speculum removal: The speculum is carefully removed from your vagina.
The test is quick, relatively simple, and generally causes minimal discomfort. You may have some light spotting or discharge afterward, but you can resume your normal activities afterward.
How to prepare for your Pap smear?
Preparing for a Pap smear is a straightforward process. Here are detailed steps on how to prepare for it:
Choose the right timing:
Schedule the appointment when you are not menstruating. The best time is usually 10 to 20 days after the first day of your last menstrual period to ensure optimal sample collection.
Avoid certain products:
For 48 hours before the test, avoid using vaginal creams, foams, or douches, as they may interfere with the test results.
Skip sexual activity:
Refrain from sexual intercourse for at least 48 hours before the test. Semen, lubricants, and certain products can affect the Pap smear results.
Inform your healthcare provider:
Inform your healthcare provider about any concerns, symptoms, or changes in your reproductive health. They can address your specific needs and provide appropriate care.
Reschedule if sick:
If you have an active infection or are feeling unwell, consider rescheduling your Pap smear. Infections can affect the accuracy of the test.
Comfortable clothing:
Wear comfortable clothing to your appointment, as you may need to undress from the waist down.
Relaxation techniques:
Practice relaxation techniques if you feel anxious. Deep breathing or meditation can help ease tension.
Ask questions:
Feel free to ask your healthcare provider any questions you may have about the procedure. Understanding the process can help alleviate concerns.
Who does not need a Pap smear?
Guidelines for Pap smears may vary depending healthcare organisations. However, some general considerations for not needing a Pap smear may include:
Women who have never had sexual intercourse
Women who have had a total hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and cervix) for non-cancerous reasons may not need Pap smears. However, this depends on the type of hysterectomy and the presence of other risk factors.
Can HPV test be done with Pap smear?
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards combining Pap smears with HPV testing for a more comprehensive approach to cervical cancer screening. This combination of tests facilitates more precise risk assessment and enables early detection of high-risk HPV strains.
FAQ
Can you get a Pap smear earlier than 25?
Generally, routine Pap smears are not recommended for women below 25 years old in Singapore. However, if you have specific concerns or risk factors, discuss them with your doctor or gynaecologist to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Where can you get HPV vaccine in Singapore?
To get the HPV vaccine in Singapore, you can consult with doctor/gynaecologist or visit clinics and hospitals where vaccination services are offered.
There are two types of HPV vaccine available:
HPV2 (Cervarix) – guards against HPV types 16 and 18, which account for 70% of cervical cancers.
HPV9 (Gardasil 9) – protect against HPT types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58, which account for an additional 20% of cancer-causing HPV types.
Do I still need Pap smears if I have had the HPV vaccine?
Yes, the HPV vaccine doesn't cover all cancer-causing HPV types, so regular screenings are still essential.
Are Pap smears covered by health insurance in Singapore?
Certain health insurance plans covers regular health screenings. For instance, AIA Vitality, Income's Lady 360 and Prudential insurances cover Pap smear.
Can I do a Pap smear during pregnancy?
Yes, Pap smears can be safely conducted during pregnancy.
What if my Pap smear results are abnormal?
Abnormal results may indicate cellular changes in the cervix. It does not necessarily mean cancer. Further tests, such as colposcopy or biopsy, may be recommended for a more detailed examination.
Is a Pap smear painful?
Pap smears are generally not painful but may cause mild discomfort. Inform your healthcare provider if you're experiencing pain.
Can cervical cancer be prevented with Pap smear?
Regular Pap smears can detect precancerous changes, allowing for early intervention and prevention of cervical cancer.
Do you still need a Pap smear after menopause?
According to MOH, a woman may discontinue screening at 69 years if her Pap smear at that age is negative and she has had two prior consecutive negative smears within the last 10 years. However, women aged over 69 years who have a history of sexual intercourse but have never undergone a Pap smear should still undergo screening.
Do you need a pap smear if not sexually active?
Pap smears are generally recommended for sexually active individuals, but guidelines may vary. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine individual screening needs.
Do virgins need Pap smears?
The need for Pap smears for women who have never had sexual intercourse may depend on individual factors and guidelines. Consult with a doctor for personalised recommendations.
HPV test vs Pap smear: What is the difference?
A Pap smear detects abnormal cervical cells, while an HPV test identifies the presence of the human papillomavirus, a common cause of cervical cancer. Both tests may be done together or independently.
How much bleeding is normal after a Pap smear?
Some spotting or light bleeding is normal after a Pap smear. If bleeding is excessive or persists, contact a healthcare provider for guidance.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
- Paragon (female doctor): +65 6735 0300
- Woodleigh: +65 8684 0153
Thomson Women's Clinic
- Bukit Batok: +65 6569 0668
- Choa Chu Kang: +65 6893 1227
- Jurong: +65 6262 8588
- Punggol: +65 6243 6843
- Sembawang: +65 6753 5228
- Sengkang: +65 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): +65 6382 3313
- Tampines: +65 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: +65 6276 1525
Dr Ryan Lee Wai Kheong
Obstetrics & Gynaecology (O&G)
Thomson Specialists Woodleigh (Women's Health)
English, Mandarin
Adept, MHC, HSBC, Alliance MediNet and 1 other

